Crawling is highly important, regardless of the size of your site.
Crawling is the key to your content being visible on Google Search Engine Results Pages (SERP).
In this article, we will explain the meaning of website crawling and the process of optimizing it to boost your content visibility.

What is Website Crawling?
Website crawling is the way spiders or search engine bots thoroughly search for and find content on your website.
Another name for bots is web crawlers.
Web-crawled content can exist in different file types, including videos, images and text.
It is important to note that search engine bots crawl content through links.
Search Process and Website Crawling
Search engines (for instance, Google) generate the most relevant pages that match queries from their index.
When you input a query into the search bar, Google’s algorithm goes through the index for the most relevant and quality pages that match it.
This implies that you aren’t directly searching the entire web. Instead, you are browsing Google index.
To clarify things better, let’s use a page on your site. Before your page shows up to someone who inputs a query or keyword relating to it, Google has to have crawled, indexed, and analyzed your page to categorize and derive ranking signals from it.
After this, your “indexed” page will show up in search results when Google believes it has “relevance” for search queries using some ranking criteria.
Thus, there are three important search processes that have to take place before any page appears on search results. They are crawling, indexing, and serving.
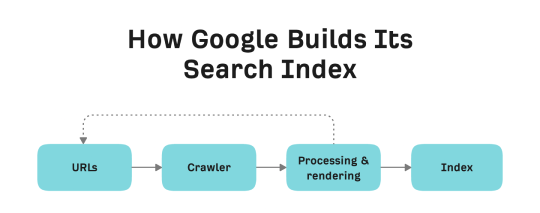
Crawling
This is the process in which the search engine bot discovers the page (becoming aware of its existence) and then revisits the page to find new updates.
Indexing
In this process, the search engine bot analyzes the page to understand its content and relevance to queries. If your page is indexed, it implies that Google has stored it in their database together with every data that has been collected.
Serving
Using the ranking algorithm, Google chooses and ranks your page in the search results according to how relevant it believes your page is to the search query
How Does a Web Crawler Work
As we have explained, a web crawler helps in finding new pages or content on the web and also checks them for new updates, if they are still in good condition, or if they are still around.
Web crawlers play the role of scanning the web to figure out its relationship, structure, and links. In simple terms, it offers a new way of understanding the framework and organization of the web.
In the next section, we will explain the way Google crawler works.
GoogleBot is the name given to Google’s crawler.
GoogleBot and Crawling
Now that we understand the function of web crawlers let’s explore the technicalities.
I will begin by explaining how Google learns about your site’s existence.
In a situation where you just launched your website, there are two major ways for Google to know about your site’s existence:
Google Search Console
Submitting your website to Google Search Console will allow Google to access a maximum of one URL (particularly the home page) to serve as a foundation for crawling other pages on your site.
Links From Other Websites
If Google has yet to discover your website, it can be found via links from other websites (as long as they have been crawled by Google).
Google will crawl these links to access your site.
How Does Google Find Other Pages on Your Website?
Once Google has discovered a minimum of one page on your site, it can now discover other pages. Let me show you how:
- Google identifies your source code.
- It identifies and retrieves your page’s internal links.
- It creates a crawl queue and adds new links to your site pages.
- Then, GoogleBot accesses the crawl queue and crawls the links one after the other.
This continues for each internal URL that is discovered until Google crawls every page on your site.
How to Optimize Your Website Crawling
Here are some ways to optimize your site crawling and avoid difficulties.
Make Sure Your Server is Fast and High-Performance
Slow servers are highly problematic. They are incapable of handling the volume of crawling Googlebot needs to do.
This is why you have to ensure your server is fast and high-performance so that it can handle the crawling process without errors or poor server response time.
Make sure that there is a green check mark next to your site host status in your crawl stats report.
Ideally, your server response time should read under three hundred milliseconds, and your 5xx error should be under one percent in your Google Search Console.
Remove Low-Value Content
If a large part of your site’s content is of poor quality, irrelevant, outdated or poorly written, it prevents crawlers from getting into newly updated or fresh content.
This is the most common cause of index bloat.
The easiest way to “declutter” your site and improve its content is to access the Google Search Console Coverage Report and then check the excluded “Crawled – currently not indexed”. It shows pages Googlebot visited but has not yet crawled.
To fix this issue, you can either merge duplicated content using a 301 redirect or delete it.
Ultimately, you must ensure that all content on your site demonstrates experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. (E-E-A-T) as this will not only improve indexability but also search visibility.
Tell Googlebot Not to Crawl Specific Pages
Although using noindex tags and rel=canonical links works well for cleaning up your site indexation, it can impact your crawl budget.
While they are quite essential, decide first if there is any need for these pages to be crawled.
If this isn’t the case, use robot.txt to disallow Google from crawling the page.
Access the Google Search Console coverage report to check situations where disallowing the search crawler is a much better option than giving an on-page indexing directive. Particularly look for ‘Excluded by noindex tag’ status.
Furthermore, check the indexing status for URLs like ‘Indexed, not submitted in sitemap’ and ‘Discovered – currently not indexed’.
Look for and block pages with no relevance to your SEO. They include:
- Non-essential/redundant images, scripts, or style files.
- Functional pages like “check out”.
- API URLs.
- URL parameter pages, like ?sort=black
- infinite spaces like the ones generated by calendar pages.
Tell Googlebot to Crawl Specific Pages
One way you can direct Googlebot to crawl pages that have SEO relevance is by using an optimized XML sitemap.
You can optimize your site map by ensuring it is constantly updated with the latest date and time to notify search engines about the recent changes on your page and whether it should be crawled again.
Facilitate Crawling via Internal Links
As I have mentioned earlier, links are highly essential for crawling.
You can begin by building and submitting your XML sitemaps to search engines. Then, build quality external links, which can be a bit tasking.
On the flip side, internal links are simpler to build and can improve your site crawl efficacy.
Thus, work on improving your site’s navigation, breadcrumbs, related content links and filters.
What is Website Crawling FAQs
What are the ways to improve my site crawlability?
- Pay attention to your site’s internal linking.
- Update your old content.
- Optimize your site structure.
- Ensure crawl errors are rectified.
- Block crawlers from accessing pages that are not relevant to your SEO.
- Improve your site loading time.
- Ensure your content demonstrates experience, expertise, authority and trustworthiness.
Why is the importance of website crawlers?
A web crawler helps in indexing site content throughout the internet so relevant pages can show up in search result pages.
What role does a crawler play in SEO?
Website crawler is highly essential in SEO since they impact your site visibility and appearance in search result pages.
If your page is yet to be visited by crawlers, search engines won’t discover, know about or position it in their results.
This can negatively affect your site traffic, revenue and conversion.
What is the meaning of indexing in SEO?
Indexing is the way search engines add your web page to their database or “index”. Before your site shows up on Google search results, it has to be indexed.
What is the importance of backlinks?
Backlinks positively impact your site ranking and authority because search engines view them as an endorsement from other websites.
The higher quality backlinks your site has, the better it ranks on search results.
What are the 4 aspects of SEO?
The four aspects of SEO are on-page, off-page, local and technical SEO. They are all important for improving your site’s visibility and traffic.
What are the important factors that impact SEO strategy?
They include URL structure, page speed, broken links redirects, website navigation and links, page speed and duplicate content.
Does Google charge for SEO?
No, SEO is free. Google does not request money for ranking your site on search engine result pages.
Google uses the E-A-T (expertise, authority and trustworthiness) guidelines, among other factors, to determine the relevance of pages in search results.
Conclusion
In this article, I have explained the meaning of website crawling and ways you can optimize crawling.
With the tips outlined in this article, you can boost your site’s SEO performance and crawl efficacy.
 PrimeGate Digital is a Result Driven Blog that strives to go beyond ‘Conventional Digital Marketing’ through digital innovation and performance marketing. We have experience working with world class brands and products.
PrimeGate Digital is a Result Driven Blog that strives to go beyond ‘Conventional Digital Marketing’ through digital innovation and performance marketing. We have experience working with world class brands and products.
